Last updated on May 10th, 2021
Marie Curie, best known for the development of the theory of radioactivity, was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist. With these 38 interesting facts about Marie Curie, let’s learn more about her inventions, personal life, contributions to science and society and Nobel Prizes.
Facts about Marie Curie’s childhood, family and education
1. Born Maria Sklodowska, Marie Curie, as we all know her today, was the fifth child of her teacher parents.
2. Due to the strained financial condition of her family during childhood,, she worked as a governess at her father’s relative’s house. There, she fell in love with the family’s son, Kazimierz Zorawski, and wanted to marry him. However, the boy’s family denied the marriage, citing the bad financial conditions of the Curie family.
3. In 1883, when Maria graduated from high school, she earned a gold medal for her academic excellence.
4. In 1891, Maria migrated to Paris, France. There, she began to pursue her education at the University of Paris, making ends meet by working part-time. It is also notable here that sometimes because of the lack of finances to buy proper meals, she fainted from hunger. However, determined to learn, she did not discontinue her studies.

5. Here, Maria adopted the French spelling of her name “Marie.”
Facts about Marie and Pierre Curie
6. Marie Curie was introduced to Pierre Curie, who later became her husband, by a Polish physicist. At the time of their meeting, Marie Curie was in need of a laboratory, and the Polish physicist was of the opinion that Pierre could afford to arrange a laboratory for Marie to continue her mission.
7. When the duo (Marie and Pierre) started working together, they developed feelings for each other. Marie refused Pierre’s initial proposal of marriage because Marie wanted to go back to her motherland and work there. Pierre declared that he was ready to move to Poland with Marie and teach French for the sake of living. Eventually, they got married on July 26th, 1895 in Sceaux.
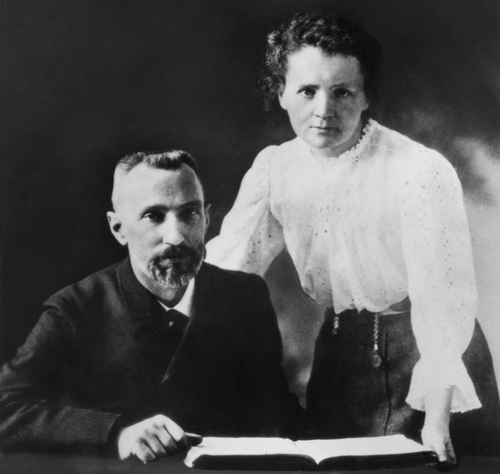

8. In 1898, Henry Becquerel discovered the “strange activity” properties of Uranium. At that time, Marie decided to investigate. During her studies, she learned that thorium also possessed such activity.
9. Pierre, intrigued and interested in the work Marie was doing, joined his spouse in mid-1898.
Discovery of Polonium and Radium
10. Discovery of Polonium: when Marie Curie realized the fact that the mineral pitchblende, which contained Uranium, was a great deal more radioactive than Uranium alone, she formed the opinion that there was some other element that caused the high level of radioactivity. The Curie duo started working on the mineral and finally extracted a black powder that was 330 times more radioactive than Uranium. They named the element Polonium, after Poland, Marie Curie’s home country.
11. Discovery of Radium: once Polonium was discovered, the duo analyzed the remaining liquid for radioactivity. They were once again amazed by the high level of radioactivity still available through the liquid. They soon started working on the compound to find the other element that caused the radioactivity. Their grueling labor yielded great results: they found radium.
12. Marie applied for a position at the Polish University of Krakow. However, being a woman, she was denied.
Regarding radium, Marie Curie said: “We must not forget that when radium was discovered no one knew that it would prove useful in hospitals. The work was one of pure science. And this is proof that scientific work must not be considered from the point of view of the direct usefulness of it. It must be done for itself, for the beauty of science, and then there is always the chance that a scientific discovery may become like the radium a benefit for humanity.”
About the subpar laboratory, the effect of radioactivity on the couple’s health, Pierre’s death and Einstein’s letter to Marie
13. The couple did not have a well-equipped and well-structured laboratory. They used a converted shed next to the School of Physics and Chemistry. The shed was poorly ventilated and was not even waterproof. German scientist, Wilhelm Ostwald, described their workplace as, “a cross between a stable and a potato shed.” Notable here is the determination and the interest of the Curies to continue their work in the field of radioactivity, despite the troubles and shortcomings.
14. Marie Curie kept a sample of radium next to her bed as a night light.

15. The Curies died unaware of the fact that the radioactive elements were damaging to their health all the time they handled and worked on them. Even the notes that they had compiled at that time and the papers that they had written are radioactively contaminated to this day. They are preserved in lead-lined boxes and when they are referenced, they are handled with the utmost care.
16. In 1906, Pierre Curie died of a road accident. This incident shattered Marie Curie; however, her firm resolution to continue her work in physics and chemistry kept her going.
17. After the death of her husband, she had a brief affair with one of Pierre Curie’s students, who was five years younger than her.
18. When the news of this affair broke out, Marie faced a great deal of criticism from the public. She started hiding from public view and lived in a friend’s house with her daughter. This incident weakened her and she lost confidence in her ability to fight back.
19. In the prestigious invite-only Solvay Conference in 1911, Marie Curie was the only woman invitee out of its 24 members. Einstein was also one of the attendees at the conference. In fact, at 32, Einstein was the youngest of the attendees.
20. After the death of her husband in 1906, she had an affair with a fellow scientist Paul Langevin. Albert Einstein, who met Marie at the Solvay Conference in 1911, wrote her a letter encouraging her during her tough time with the public. Here is a copy of the letter by Albert Einstein

About Marie Curie’s use of X-ray units during WWI, the French honor, the cause of death and more…
21. Marie Curie created X-ray units that were helpful in treating more than a million soldiers in World War I. She established X-ray booths and also operated mobile X-ray units. The units were known as petite curies (“little curies”).
22. Marie Curie received a stipend from the French government after the 25th anniversary of the discovery of radium. She stopped using the stipend once other forms of financial assistance became available to her.
23. Marie Curie’s daughter, Irene Joliot-Curie, also won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1935, jointly with her husband.
24. Money was not something that mattered a lot in the life of the couple. They just needed it to meet their needs. They also decided not to patent the radium-isolation process for the sake of the scientific community.
25. The duo often refused awards and medals.
26. Marie was so selfless that Einstein said about her that she probably was the only person whom fame and money could not corrupt.
. . . continue reading on the next page.
