Last updated on January 18th, 2023
What is your favorite chemical element? Is it carbon? Maybe nitrogen? Everyone needs a favorite element. Why silicon? Well it’s one of the more versatile elements out there. It’s also the reason why you can use a computer. Your favorite glass or dish most certainly has silicon in it. If silicon weren’t your favorite element before, here are 50 facts about silicon that may help you change your mind about this very common element.
50 Facts about Silicon
1. Silicon is a chemical element. It has position 14 on the Periodic Table. This means it has 14 protons and electrons. It’s chemical symbol is Si, for “silicon” – one of the very obvious symbols, not a head-scratcher like Pb (lead).
2. Silicon is a close chemical relative of elements like carbon, tin and lead. It shares many of the same chemical properties as these elements. Chemists can often make silicon equivalents of carbon-based molecules.
3. Pure silicon is a bluish-gray solid with metallic shine. Even though it looks like a metal, pure silicon does not conduct either heat or electricity very well.
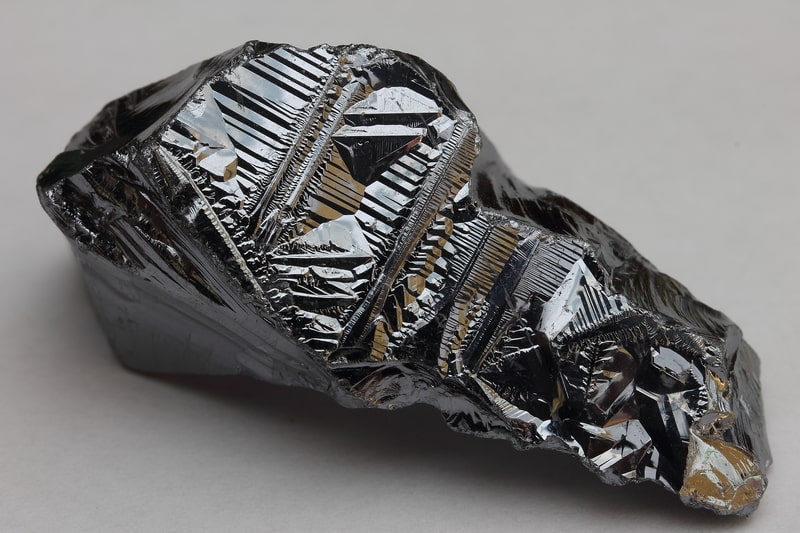

4. Silicon is the eighth most abundant element in the universe by mass. More abundant elements include hydrogen, helium, oxygen, carbon, neon, iron, and nitrogen.
5. Some scientists speculate that the biology of other planets may use silicon rather than carbon as the building blocks of life. On Earth, there are no organic carbon-silicon molecules found in nature. Finding a silicon-based lifeform would be incredible advance of our knowledge of how biology works.
6. Silicon is everywhere on this planet. Almost literally everywhere. It shows up in soil, sand and rocks. It is the second most abundant element in the Earth’s rocky crust, making up about a quarter of the total weight. Silicon-containing minerals make up close to 95% of the mineral content of Earth’s crust.
7. Silicon dioxide, or silica is the most common form of silicon found in nature. You may know of it in its more common form as quartz rock. It’s also a major component of sand and is used to make typical glasses like window panes and bottles.

8. One silicon compound, silicon carbide, is used to make steel and other metal alloys much stronger and resistant to corrosion. This accounts for much of the world’s production of silicon.
9. China is the world’s biggest producer of silicon, producing about 6000 tons of silicon per year. The United States is fifth.
10. One of the most important uses of silicon is to make computer chips and other electronic devices. Computers depend on the tiny highly precise amount of impurities like phosphorus, boron and nitrogen that are added to silicon so that they can, well, compute things. Without silicon it would be much more difficult to build the computing devices we have all become used to having around. Some researchers are attempting to replace silicon with materials like diamond for computer chips.
11. Diatoms are a type of single-celled ocean dwelling algae that produce a silica shell naturally. These shells can take on a wide array of beautiful shapes such as spheres and pyramid shapes. Diatoms absorb billions of tons of silica from the waters they live in to produce these shells. When these organisms die, the shells create what is called diatomaceous earth which has a wide variety of uses.
12. Most living things have some form of silicon within them in. Animals, like us, only have trace amounts. Pure silicone is not toxic to ingest for humans, but there are silicon compounds which are dangerous.
13. Pure silicon is virtually never found in nature. Silicon is highly reactive with oxygen. Usually only silicon compounds are found. These take on the form of minerals like quartz or other silicates.

14. Some people may confuse “silicon” with “silicone”. Silicon is an element, silicone is a silicon compound that contains silicon, carbon and hydrogen. The word “silicone” was first used in 1901.
15. Well, then, what is silicone? Like its cousin carbon, silicon atoms can form long rubbery chains. Silicone may be most famous for its use in breast implants, but it also has its other uses in medicine as well.
16. Silicones have important uses in industry for use as sealants and lubricants because of their high flexibility and thermal stability.
17. Silicone gels are widely used in kitchen goods because of its non-stick properties. Your non-stick spatulas and brushes are probably made of silicone gel.
18. Silicone is widely used for medical implants because of its high bio-compatibility meaning that it is much less likely to trigger bad reactions with your body than other materials.
19. Silicone also makes rubber goods more flexible and resistant to changes in temperature.
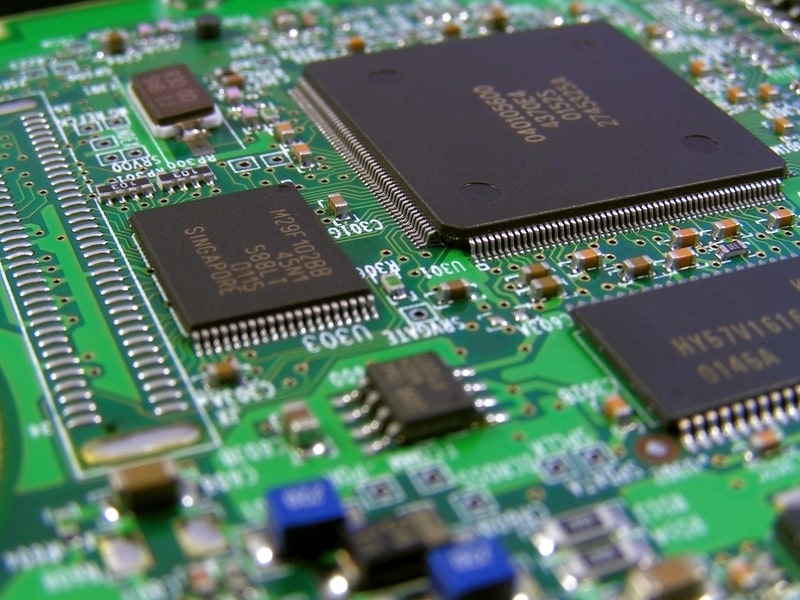
20. Silicon can also imitate its cousin carbon in other ways. The silicon equivalent of methane, silane, is used to etch circuits onto computer chips and other similar devices because it can dissolve silicon dioxide easily.
21. Silicon is commercially produced by reacting silica and carbon together at high temperatures in an electric-arc furnace to create pure silicon and carbon dioxide. This process is then further refined to produce high-quality silicon crystals for use in the semiconductor industry. Less pure silicon from this process is used to make steel and other products.
22. Computer chips are made from very thin slices of ultra-high purity silicon crystals called wafers. Very precise amounts of specified impurities are added to make the silicon more electrically conductive in specified places. These circuits form the foundations of the transistor devices that make modern computing possible. This process takes place in ultra-clean environments. People who work in these environments have to wear special suits to prevent contaminating the chips.
23. Computer chip manufacturers need extra high purity silica to make computer devices. Even small amounts of impurities can ruin the delicate structures required for today’s high performance computers. Manufactures like to keep the sources of their silica secret to maintain a competitive advantage.
24. Silica is an important component of concrete. Silicate minerals, along with a binder, help to give concrete its strength and durability. The ancient Romans were the first to use concrete with silicates and many of those structures still exist today. Silicates are part of the reason why.
25. Having a good source of high-quality silicon may be important in the future of alternative energy production. Solar cells are made using high purity silicon to trap light energy and convert it to electricity. Creating pure silicon for use in solar panels is expensive though. Alternatives to this include using less efficient polycrystalline silicon to make solar cells. Research is ongoing in how to make these devices much cheaper, efficient and more readily available for use in homes and other buildings.
26. Silicon is a component of materials like asbestos. Asbestos was formerly commonly used as an insulating material and as a fire retardant in homes and businesses. It was discovered that breathing in asbestos fibers can cause serious damage to the lungs. Asbestos has since been banned as a building material.
27. Silicon has a dual character. It can function as both a metal and a non-metal. This is described by chemists as a “metalloid”, not quite a metal, and not quite a non-metal. It is shiny like a metal but is also quite brittle like most non-metal elements. It is also only weakly conductive at room temperature – somewhat in-between metals and insulating materials.
28. Silicon is essential for plant life and is readily absorbed by many plants. It is an essential component of the cell walls of many plant species.
29. Foods like beer and oats contain silicon absorbed by plants. Silicon is also an important mineral for humans and other animals in small amounts.
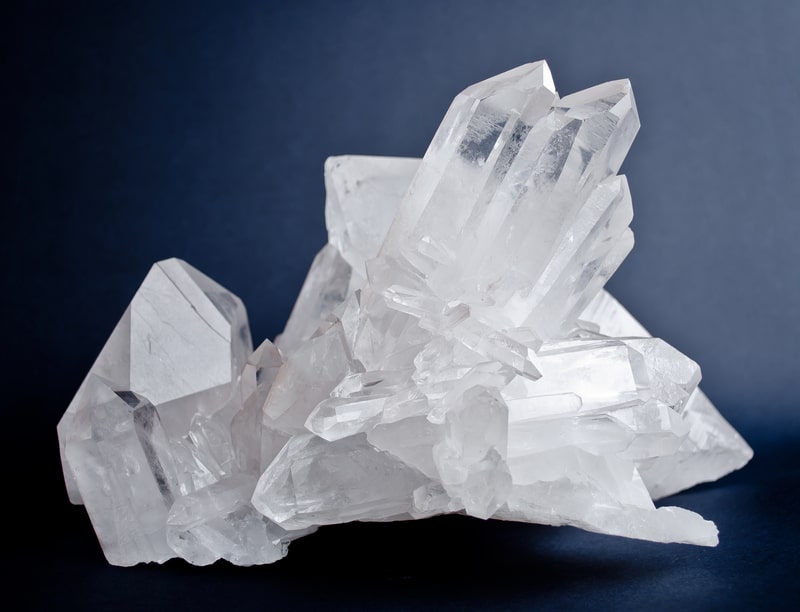

30. Silicates, like quartz, have extremely high melting points. For example, quartz melts at about 1650 degrees Celsius. This makes silicate glasses good for applications where high heat is necessary. For example, you can melt iron or other metals in a quartz container without damaging the container.
31. Ground silicates are highly absorbent materials. They have a high surface area and are often used to purify water and other materials. Impurities stick to the surface of the material and are filtered out of the water as it passes through the filter.
32. One surprising place to find silicon and related compounds is in shampoos and soaps.
33. Minerals other than quartz that contain silicon are feldspar, mica and flint.
34. Silica is highly resistant to corrosion. Only a few powerful chemicals can dissolve it. Manufacturers often use it as a coating to prevent materials from degrading from environmental exposure.
35. Extremely tiny particles of silicon, known as quantum dots, shine brightly in response to florescent light. The brilliant and almost pure colors emitted make quantum dots nearly ideal for displays. The color of light they emit is dependent only on the size of dots. This makes them useful for new kinds of television monitors and other electronic displays.
. . . continue reading on the next page
